HOw was Standard based education or curriculum introduced in PNG? Introduction of Standard Based Education IN PNG Introduction of Standard Based Education IN PNG The introduction of SDE or SDC followed the PNG Governments NEC Decision No.194/2008
Outcome-Based Education in schools throughout the country. This decision is contained in the National Executive Council (NEC) Decision No.194/2008 item 12 which states: “The Committee agreed that the outcomes-based education and the elementary system should be done away with. That an exit strategy be established, especially for the elementary system.”(p.2).
learning, and identify the gaps. Based upon the evidence provided from this analysis, an OBE exit strategy will then be developed and implemented. This is the Department of Education’s response to National Executive Council Decisions to review and exit Outcome Based Education and the development of a new curriculum. This includes: • OBE Exit Consultative Forum-Resolutions and Recommendations. • Setting up of the OBE Exit Technical Working Team (OBEETWT) and the OBE Exit Secretariat (OBEES) who began their work on the Report of the Task Force for the Review of Outcomes Based Education.
0 Comments
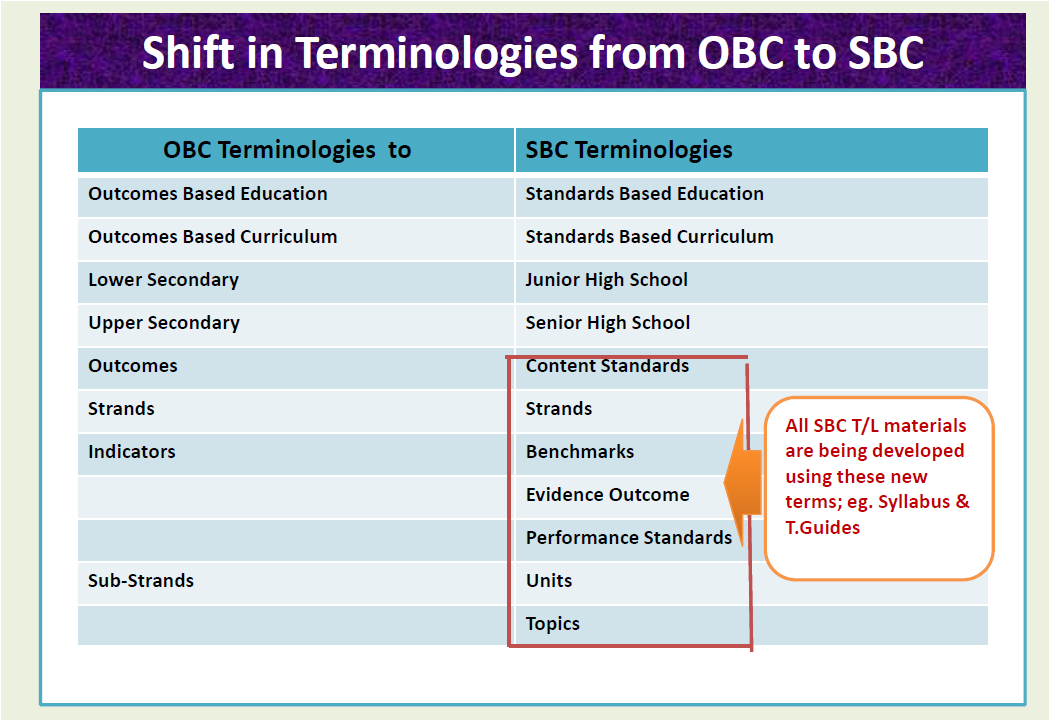 Shift in Terminologies from OBC to SBC- The following terms have changed from the outcome based curriculum to Stanard Based Curriculum.
Below are the differences between Content Standards, Benchmarks and Performance Standards used in Standard Based Curriculum.
Content Standards
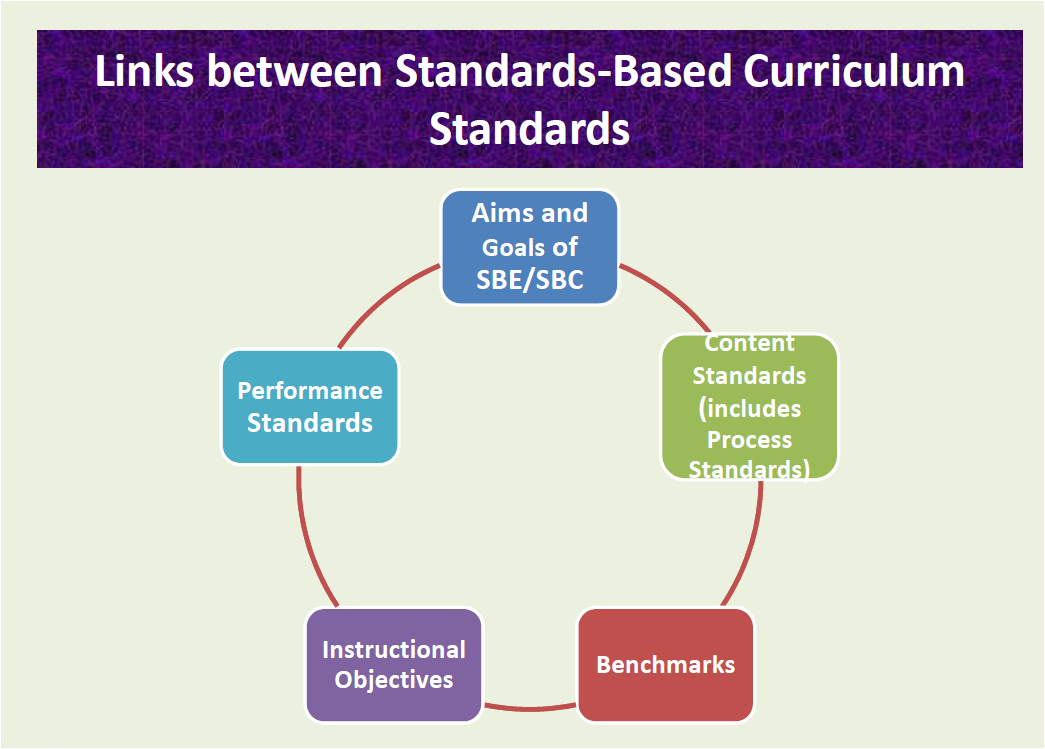 Below are the Types of Standards in Standard Based Curriculum (SBC)
What are the Designs used in SBC Development?
Three curriculum designs have been used to develop the Standards-Based Curriculum 1. Broad Fields Curriculum Design
The Academic Disciplines Design (Subject Design) was chosen by the National Curriculum Standards Framework Task Force to enable students progressing to grades 11 and 12 to study in-depth the various subject disciplines, particularly in mathematics and science, to prepare them for careers, higher education and citizenship. Assessment as Learning (AaL)
Finally, let us consider assessment as learning. AaL is part of assessment for learning and both approaches are formative. From teachers’ feedback to the students, they (the students) become more responsible for their learning. The students must, however, be guided by teachers. According to Berry (2008), AaL leaves the onus for learning on students and “encourages and demands deep learning on the part of the students” (Berry, 2008, p. 34). Berry (2008) highlights the fact that “students are their own assessors and they personally monitor and critically review what they are learning. With this monitoring and critical review, they make adjustments, adaptations, and even major changes to what they understand” (Berry, 2008, p. 34). The definition of the word ‘assessment’ may have shifted from that of cooperation to competition. There is a need to revisit the original meaning of the word and devise assessment tasks that would promote student learning. The Latin word ‘assidere’ was all about assessment for learning where there was a good sense of students working together and sharing their ideas. Teachers would sit beside students and give one to one assistance where necessary. This is assessment for learning at its best where learning is improved.
In this approach the focus is on the process of learning and teachers’ role in the classroom become very significant in ensuring that learning takes place. Assessment for Learning (AfL) should be continuous and formative. The Wikipedia puts an explanation of Standard based assessment this way.
"In an educational setting, standards-based assessment is assessment that relies on the evaluation of student understanding with respect to agreed-upon standards, also known as "outcomes". The standards set the criteria for the successful demonstration of the understanding of a concept or skill". Standard based Assessment consist of three components.
1. Assessment of Learning (AoL) Berry (2008, p. 32) points out that “assessment of learning is mostly used for making summative judgment of students’ performances.” In addition, the author stresses that AoL is used to compare student’s performance against goals and standards or each other (Berry, 2008). In other words, AoL takes place at the end of the course and is mainly concentrating on the product of learning. In PNG context, the national examinations in grades 8, 10 and 12 are classical examples of AoL. The results of the examinations are used to select students to the next level of education based on their performances. The grade 8 students receive Basic Education Certificate, grade 10 students receive Lower Secondary School Certificate and grade 12 students receive Upper Secondary School Certificate. The certificates are awarded to students to confirm that they have completed the nationally prescribed subjects in the appropriate grades. In other words the national examinations in PNG have two main functions: for certification and for selection to the next level of education Many schools and education systems still place significant priority on measuring learning outcomes with scores, grades and marks. But this focus and emphasis often misses a bigger picture, and doesn’t take into account the process of learning. Assessment for Learning (i.e. formative, classroom, school-based assessments) focuses on information and feedback for the students to help progress and reach their learning goals, rather than evaluating student achievement. In addition, it allows teachers to use this information to improve the quality and effectiveness of their teaching. According to Stewart Monckton, Research Fellow at the Australian Council of Educational Research (ACER), ‘the key aspect of AfL is that it places meaningful and timely assessment and feedback at the heart of everyday classroom teaching.’ Doug McCurry, Senior Research Fellow at ACER concurs, ‘I know of no other approach to teaching and learning that offers such potential improvements in learning.’
Papua New Guinea is doing away with the Outcome Based Education (OBE) and now implementing the Standard Based Education (SBC).
Structure of School System The Government has embarked on free and compulsory education in 2015 and the level of resources will need to complement the school structure to enhance the standards of education and to keep the children in school. The Standard Based Education structure is called 2-6-6- Structure as outlined below.
|
|
- Home
- Education News
- Education Talk
- Exam Questions
- Teaching Jobs
- Scholarships
- Education Department
-
Study in PNG
- Study Abroad
- DHERST
- Institutions
- Payslips Online
- Curriculum
- About
- Contact
- School Profile Application
- Research & References
- Links
- Disclaimer
- Privacy Policy
- PNG Education Resources
- MyPaySlip App for PNG Teachers & Public Servants
- L&L Exam Questions
- Maths A Exam Questions
- Maths B Exam Questions
-
List of Primary Schools in Gulf Province
- Primary Schools in Western Province
- Primary Schools in Milne Bay Province
- Primary Schools in Oro Province
- Primary Schools in Southern Highlands Province
- Primary Schools in Eastern Highlands Province
- Primary Schools in Simbu Province
- Primary Schools in Western Highlands Province
- Primary Schools in West Sepik Province
- Primary Schools in East Sepik Province
- Primary Schools in Madang Province
- Primary Schools in Morobe Province
- List of Primary Schools in West New Britain Province
- List of Primary Schools in East New Britain Province
- List of Primary Schools in New Ireland Province
- List of Primary Schools Schools in Bougainville
- List of Primary Schools in Manus Province
- List of Primary Schools in Enga Province
- List of Primary Schools in Hela Province
- List of Primary Schools in Jiwaka Province
- Grade 8 Examination Questions online
-
Grade 12 Examination Topics and Units
- Chemistry Exam Units
- Physic Exam Topics & Units
- Biology Exam Topics and Units
- Language and Literate Examination Topics and Units - PNG
- PNG Advance Mathematics Examination Topics & Units
- General Mathematics Examination Topics and Units - PNG
- PNG Economics Examination Topics and Units
- PNG History Examination Topics and Units
- Applied Science Exam Topics
- Geology Examination Topics
- Geography Exam Topics
- Legal Study Exam Topics
- Business Studies Exam Topics
- ICT Examination Topics & Units
- Accounting Examination Topics
- Types of Job Interviews
- Simbu Teachers College
- Study at UOG
- STEM Education PNG
- FODE Admission
Home : About : Education News : Research Papers : Bibliographies : Disclaimer : Institutions : Contact Us : Privacy Policy
|
Search Education Database >>
|
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

